We round up the best new features of Fedora 40 release.
Fedora 40 is officially released on April 23, 2024. Overall, there are no such dramatic changes in Fedora 40. The most important change in Fedora 40 is the introduction of the KDE Plasma 6 desktop environment (for KDE edition), which brings a host of new features.
Apart from that, mostly the core changes catered to system hardening, core package upgrades and security improvement. Let’s briefly round up the new features.
Table of Contents
Fedora 40: New Features
Kernel updates
At the core, Fedora 40 is powered by Linux Kernel 6.8 which was released on 10th March. This is the latest mainline Kernel as of publishing this. Hence, with this release, you are bound to get the latest features and hardware updates. If you are using the new CPU, GPU or other hardware, you should definitely check out this Kernel 6.8 feature guide.
GNOME 46
The Fedora 40 workstation edition features GNOME 46. GNOME 46 is powered by GTK 4.13 and libadwaita 1.4.2. Most of the changes in GNOME Shell in version 46 are under the hood updates, catering to bug fixes and performance improvements.
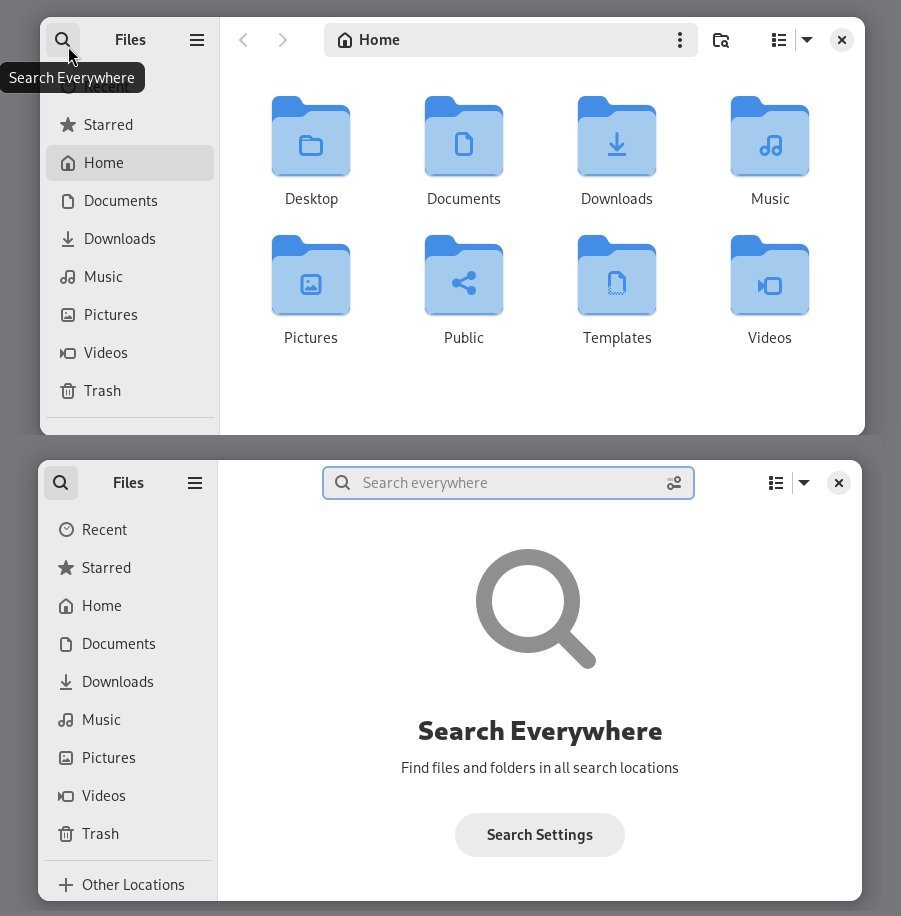
One of the key changes that Nautilus brings as part of GNOME 46, is the addressing of the long-standing performance issue when you change the view (say from list to grid). Each time you change the view, Nautilus tries to reload the entire directory.
In addition, the search function of Nautilus gets a complete overhaul. Search current folder: This replaces the original search button and remains focused on finding files within the currently displayed directory. Global search: A brand-new button added to the left pane, allowing you to instantly search your entire file system for the desired file(s).
For more such features of GNOME 46, you can read my official feature guide.
Detecting duplicate IP
The presence of duplicate IPv4 addresses in a physical network can cause networking issues, which can be difficult for users to diagnose. RFC 5227 outlines a mechanism for detecting address conflicts, known as Address Conflict Detection (ACD), which involves sending ARP probes for each IP address a host wants to use. In Fedora 39, ACD is disabled by default but can be enabled by setting the “ipv4.dad-timeout” property to a positive value in a connection profile. The Fedora team is enabling ACD by default in Fedora 40, with a default value of 200ms. This change only affects IPv4; IPv6 always performs a duplicate check for each address that is configured.
Few DNF5 updates
The next version of the DNF package manager, DNF 5, aims to improve performance and reduce memory usage and disk footprint compared to DNF. Although the switch to DNF 5 was initially planned for Fedora 39, it has been postponed to a later release, likely Fedora 41.
As a result, the team plans to start using DNF 5 for building Fedora in the interim, beginning with the package management features required for buildroots in Mock. This approach will enable large-scale testing of DNF 5’s stability and performance, providing valuable data for future development.
Another change in DNF aims to modify the default behavior so that it does not download filelists, which are metadata that describe the files contained within each package. These filelists are often not required for most use cases, and they can significantly slow down the user experience due to their large file size. By excluding filelists from default downloads, DNF can potentially improve performance and enhance user satisfaction.
/var/run to /run
Around 10 years ago, the location of system runtime files’ actual path changed from /var/run to /run. However, the policy was maintained in a way that retained old entries and continued to use the incorrect path, while the actual path was managed through a file equivalency feature.
This situation can create confusion for sysadmins who may not know which path to use. To address this issue, the Fedora team recently migrated the /var/run selinux-policy entries to /run, eliminating the technical debt.
Pytorch
Fedora 40 offers PyTorch as part of the Fedora 40 repository. The objective of packaging PyTorch for Fedora is to make this open-source machine learning framework readily available and easily integrable within the Fedora Linux ecosystem.
This approach increases the accessibility of PyTorch for Fedora users, creating a favorable environment for developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to utilize the capabilities of this robust machine learning framework.
wget
GNU Wget2 is the updated version of Wget, featuring a modern implementation based on a new library called libwget2. The proposed switch from Wget 1.x to Wget2 aims to transition to a more actively developed and feature-rich implementation, offering a better interface for utilizing Wget’s functionality.
The main advantages of switching to Wget2 include a cleaner codebase that adheres to modern development and maintenance practices, such as unit testing and fuzzing as a security measure. Users can also expect improved support for newer protocols over time, as they can be more easily and quickly integrated into Wget2 compared to Wget.
Other key updates
- Another minor change is the Firefox desktop file from firefox.desktop to org.mozilla.firefox.desktop.
Firefox needs to provide desktop file in expected format to pair DBus service and Gnome search service together to make Gnome search service work. - Fedora Cloud Edition images will be built with Kiwi, which will replace the unmaintained ImageFactory tooling that is currently being used to build the cloud base images.
- The Fedora website currently uses the term “Immutable Desktops” to regroup all desktop, rpm-ostree based Fedora variants. The term “immutable” is confusing to users, has been the source of a good deal of confusion, and does not accurately reflect the advantages of those variants. Hence, the team introduced “Atomic” naming convention for the desktop flavors. For example, an Atomic variant can be named as Fedora LXQt Atomic.
Applications and tool chains
The native applications and tool chains are updated according to their respective latest versions:
- Firefox 123
- Golang 1.22
- LLVM 18.0
- System JDK – java-21-openjdk
- Ruby 3.3
- GNU tools: gcc 14.0, binutils 2.41, glibc 2.39, gdb 14.1
- PostgreSQL 16
- PHP 8.3
- Python 3.12 (3.7 is removed as EOL)
Desktop environment updates
Fedora Linux features almost all major desktop environments and window managers as “Spins”. This release brings KDE Plasma 6 “megarelease”, whereas the Xfce 4.18 version with the latest fixes and improvements graces in the Xfce edition. You can also get the latest version of MATE desktop, Budgie desktop, LXQt, i3 and Sway spins.
Download
You can download the ISO for workstation and other flavours on this below page.
Closing Notes
This release may feel like a calm one. But all the changes, mostly under-the-hood, strengthen the Fedora base for all use cases. If you used Fedora Linux in the recent past, you may felt that it became more stable and secure. Fedora 40 changes will also contribute to that.